MERCATORSOLD
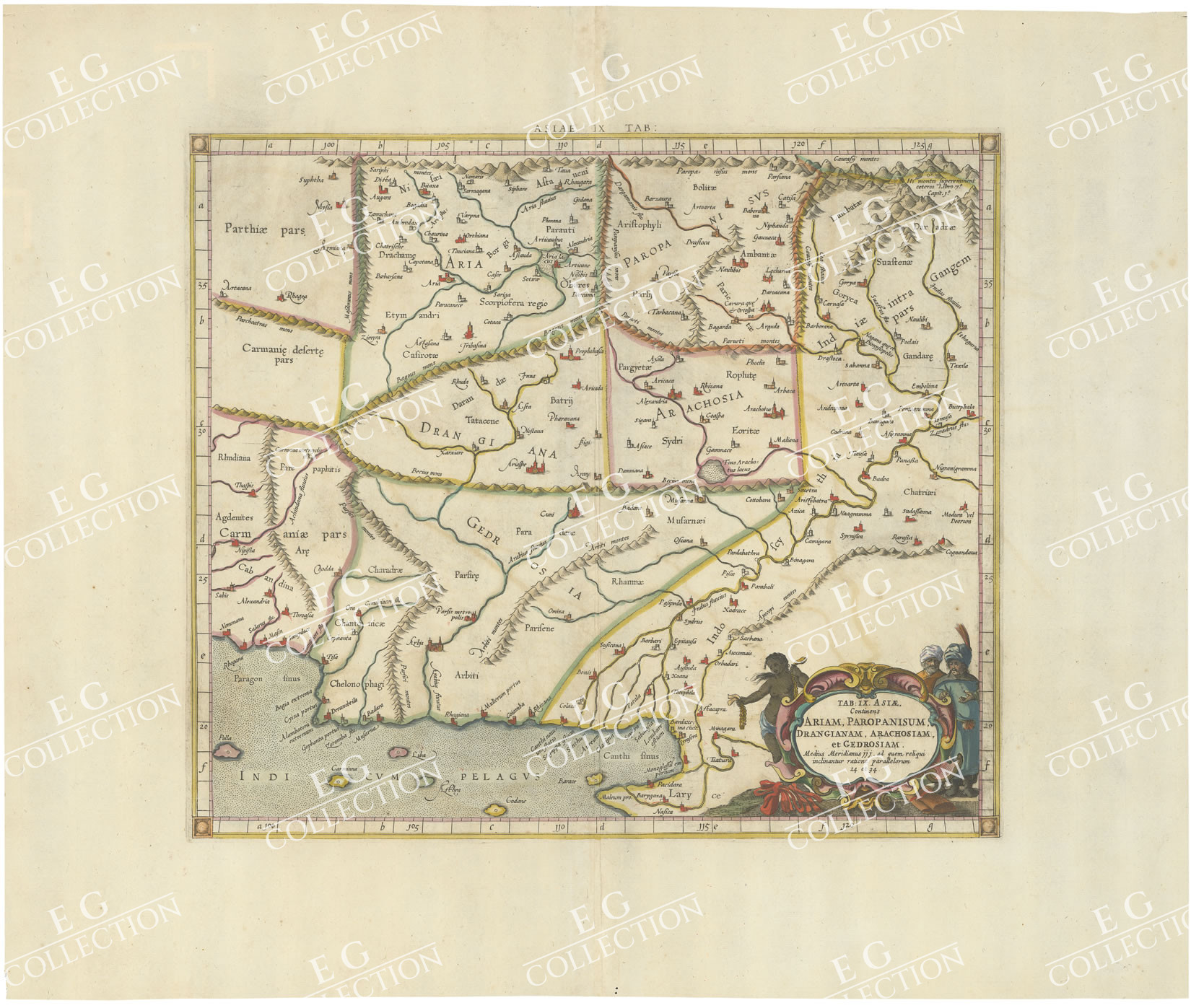
TAB: IX ASIAE Continens ARIAM, PAROPANISUM, DRANGIANAM, ARACHOSIAM et
GEDROSIAM
MERCATOR, Gerard
c. 1697
45×32 cm
A striking Ptolemaic map of Central Asia, centered on the Indus River.
The map extends from the Gujarat region in the east to west of Karchi, the north to the
mountains.
Mercator originally published this map in his 1578 edition of Ptolemy’s Geographia.
Although Mercator is most renowned today for the projection he popularized and for first
using the term Atlas for a collection of maps, Mercator’s great dream was to produce an
improved and updated edition of Ptolemy’s maps. Achieved toward the end of his lifetime,
the maps were beautifully engraved and are widely regarded as one of the best and most
accomplished editions of Ptolemy, albeit one of the last.
Gerard Mercator Biography:
Gerard Mercator is one of the most famous cartographers of all time. Mercator was born in
Flanders and educated at the Catholic University in Leuven. After his graduation in 1532,
Mercator worked with Gemma Frisius, a prominent mathematician, and Gaspar a Myrica, a
goldsmith and engraver. Together, these men produced globes and scientific instruments,
allowing Mercator to hone his skills.
With his wife, Barbara, Mercator had six children: Arnold, Emerentia, Dorothes,
Bartholomeus, Rumold, and Catharina. In 1552, Mercator moved to Duisburg from
Leuven, where he lived for the rest of his life. In 1564, he was appointed the official
cosmographer to the court of Duke Wilhelm of Cleve.
Mercator’s most important contribution was the creation and popularization of a projection
which now bears his name. On Mercator projection maps, all parallels and meridians are
drawn at right angles to each other, with the distance between the parallels extending
towards the poles. This allowed for accurate latitude and longitude calculation and also
allowed navigational routes to be drawn using straight lines, a huge advantage for sailors
as this allowed them to plot courses without constant recourse to adjusting compass
readings.
Mercator’s other enduring contribution to cartography is the term “atlas”, which was first
used to describe his collection of maps gathered in one volume. The Mercator atlas was
published in 1595, a year after Mercator’s death, thanks to the work of his sons,
particularly Rumold, and his grandsons.
$ 400,00
Out of stock




 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.